How to create an interactive Python lab with Pytest?
We'll divide this part into 5 sections:
- Creating lab metadata
- Setting up lab defaults
- Setting up lab challenges
- Setting up test file
- Setting up evaluation script
Introduction
This guide would assume that you already have created an interactive course from your instructor panel. If not, go here and set it up first
Step 1 - Creating lab metadata
- Add a new item lab in your course curriculum page
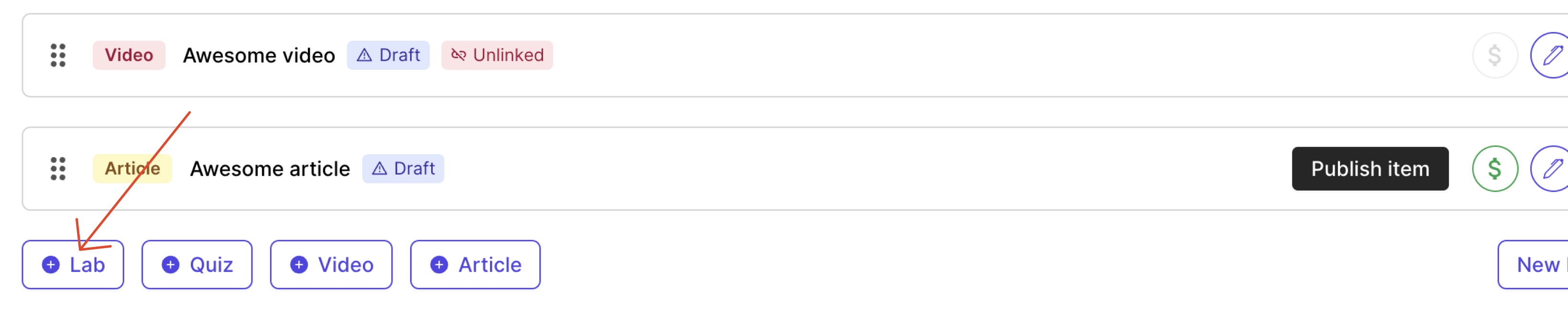
A new lab item gets added. Click on the edit pencil button on the right. This should open the lab library widget in your instructor panel.
You should now be able to write a quick lab name and press on "Create Lab" button. This would create a lab you would be able to edit.
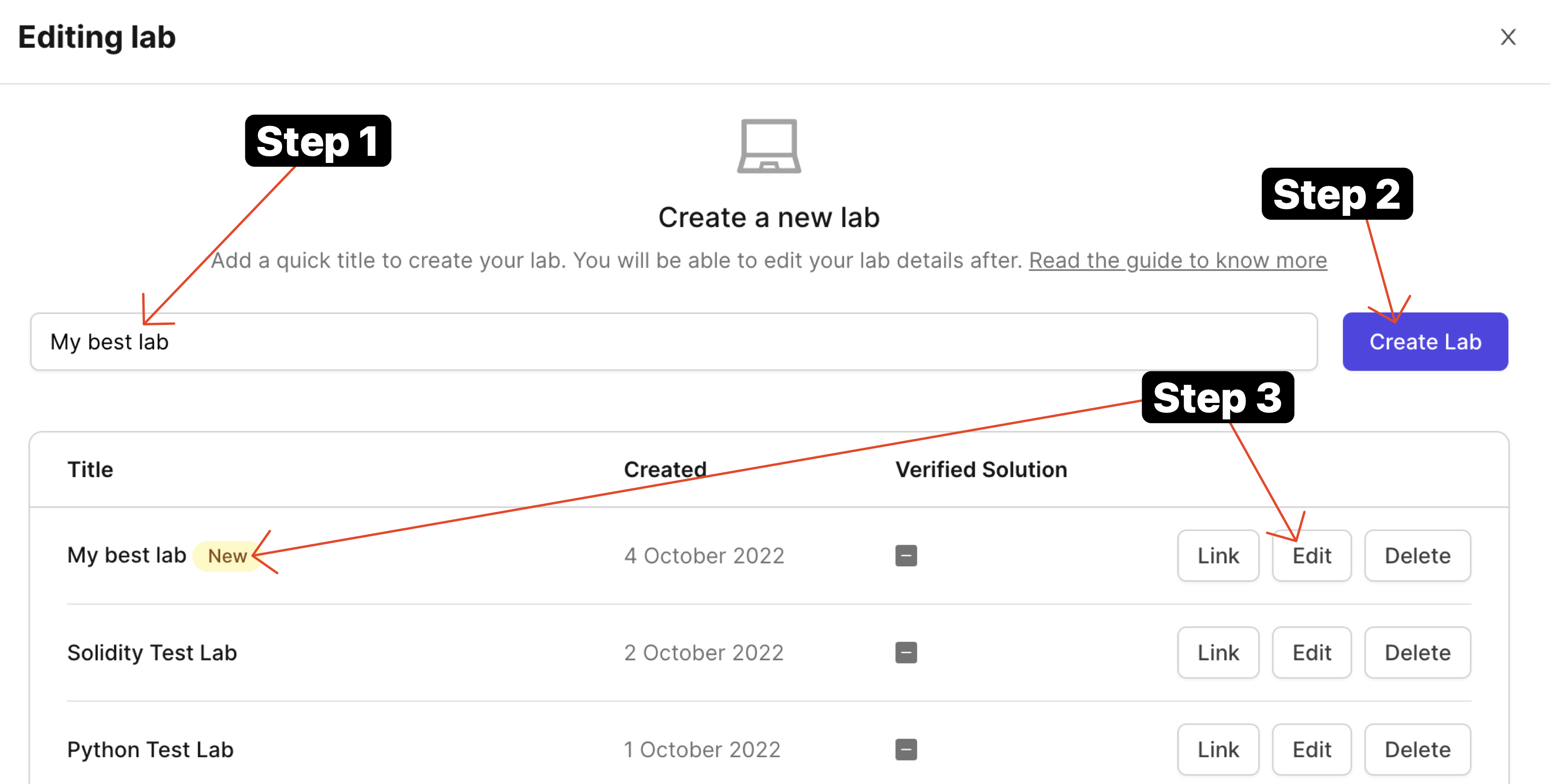
- Once it is created, click on the "Edit" button and you'll arrive at lab designer view.
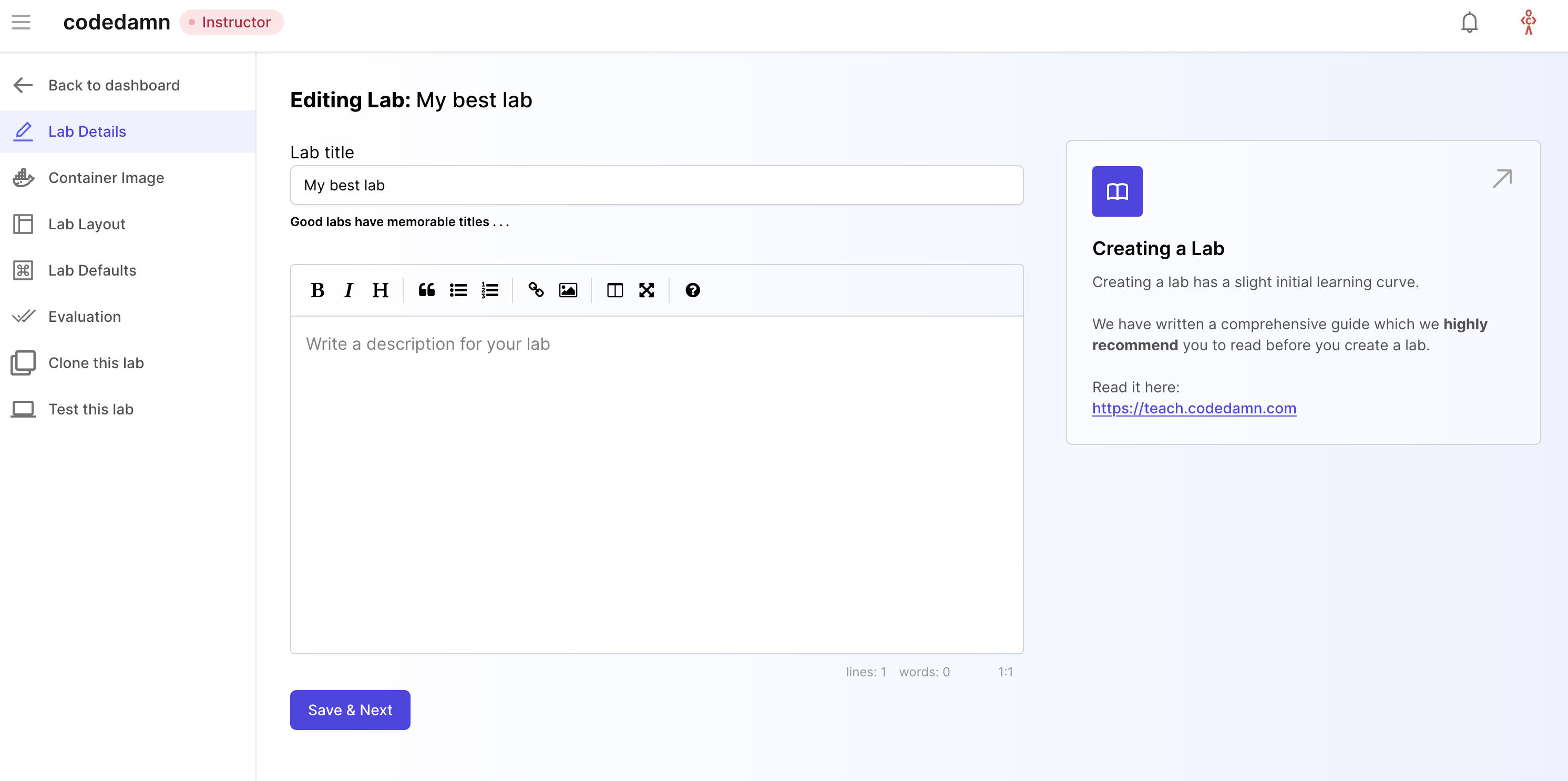
This is where you will add metadata to your labs and setup your labs for evaluation. Let's take a look at all the tabs here.
Lab Details
Lab details is the tab where you add two important things:
- Lab title
- Lab description
This can be used as a helper text area for your lab. You should include as much detail as possible here to make it easier for the user to understand and solve your coding lab.
Let's move to the next tab now.
Container Image
Container image should be set as Python 3.8 for Python labs. The following software are available by default in this image:
- Python version 3.8
- Pip 3
- Packages: pytest and pytest-json-report for Python unit testing
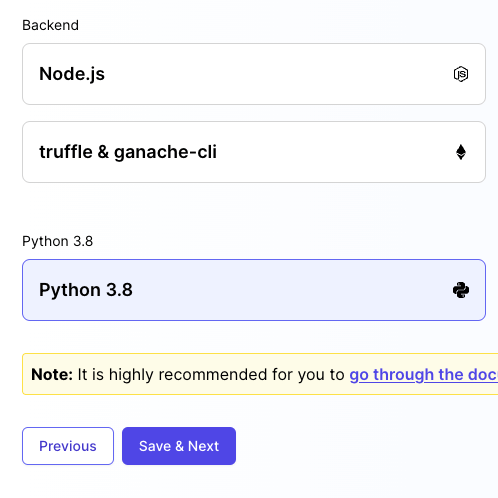
We will setup and install a Python environment on the runtime.
Lab Layout
Lab layout can be used to set a default layout in which the lab boots. We currently support the following layout types:
Terminal + IDE + Browser
This would include everything codedamn has to offer - a terminal at the bottom, an IDE in center (powered by Monaco on desktops, and CodeMirror on mobile phones), and a browser preview of (ideally) what user is working on. This is best if your playground runs a HTTP server.
Terminal + Browser
This layout is for times when you don't need IDE in place, and only want something hosted inside a browser - like a XSS challenge.
Terminal + IDE
This layout is for backend programming without website UI. This would only include a terminal and an IDE - like VS Code. For example - headless E2E testing, writing Python scripts, discord bots, etc.
Terminal only
This would not include anything, except for a terminal. Best for Linux/bash labs where you want users to exclusively work with terminals only.
TIP
You can configure the layout through .cdmrc file too. More information here
Step 2 - Lab Defaults
Lab defaults section include how your lab environment boots. It is one of the most important parts because a wrong default environment might confuse your students. Therefore it is important to set it up properly.
When a codedamn playground boots, it can setup a filesystem for user by default. You can specify what the starting files could be, by specifying a git repository and a branch name:
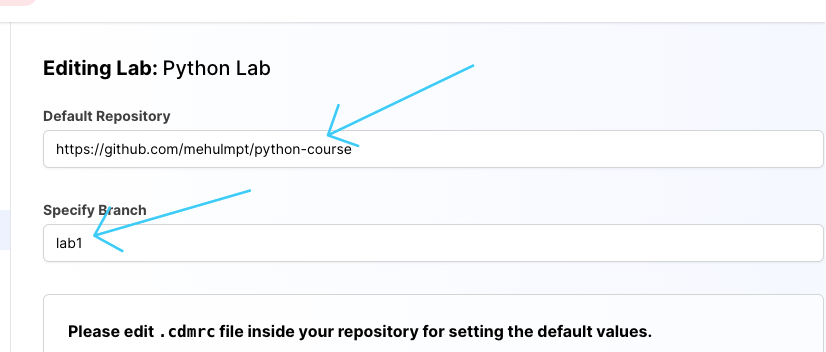
You will find a .cdmrc file in the repository given to you above. It is highly recommend, at this point, that you go through the .cdmrc guide and how to use .cdmrc in playgrounds to understand what .cdmrc file exactly is. Once you understand how to work with .cdmrc come back to this area.
Step 3 - Lab challenges
Next step is to setup challenges and evaluation for your lab. This is the part where your learners can learn the most because they will have to pass certain challenges.
TIP
It is highly recommended for you to watch the video below to understand the architecture
This is the biggest advantage of using codedamn for hosting your course too - to make them truly interactive and hands-on for your users.
Let's start by setting up challenges.
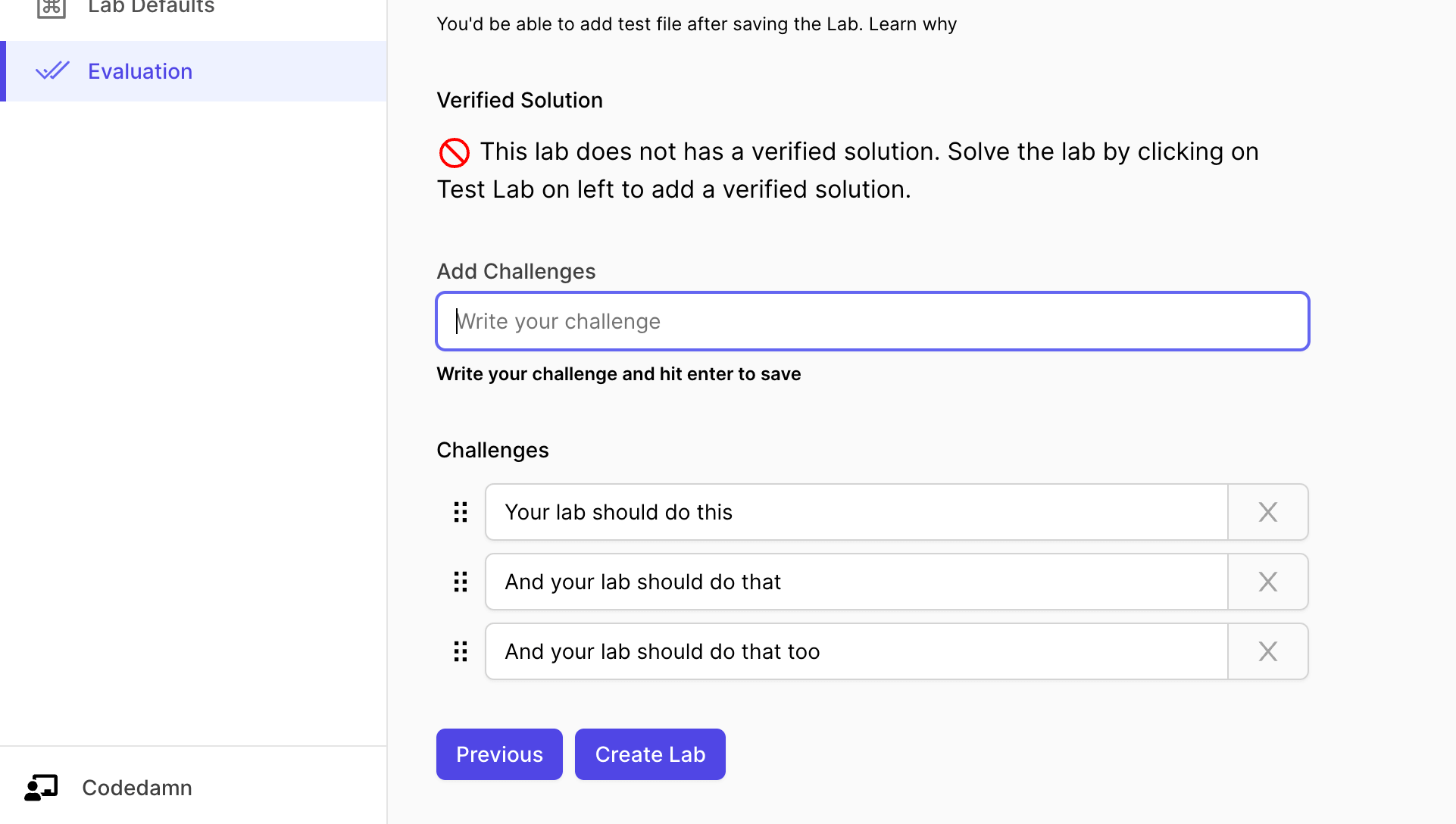
The interface above can be used to add challenges to your lab. You can also add hints to every single challenge you put here.
TIP
When the user runs the lab but fails a few challenges, the hint for that particular failed challenge is displayed to the user.
Step 4 - Test file
Once you save the lab, you will see a button named Edit Test File in the Evaluation tab. Click on it.
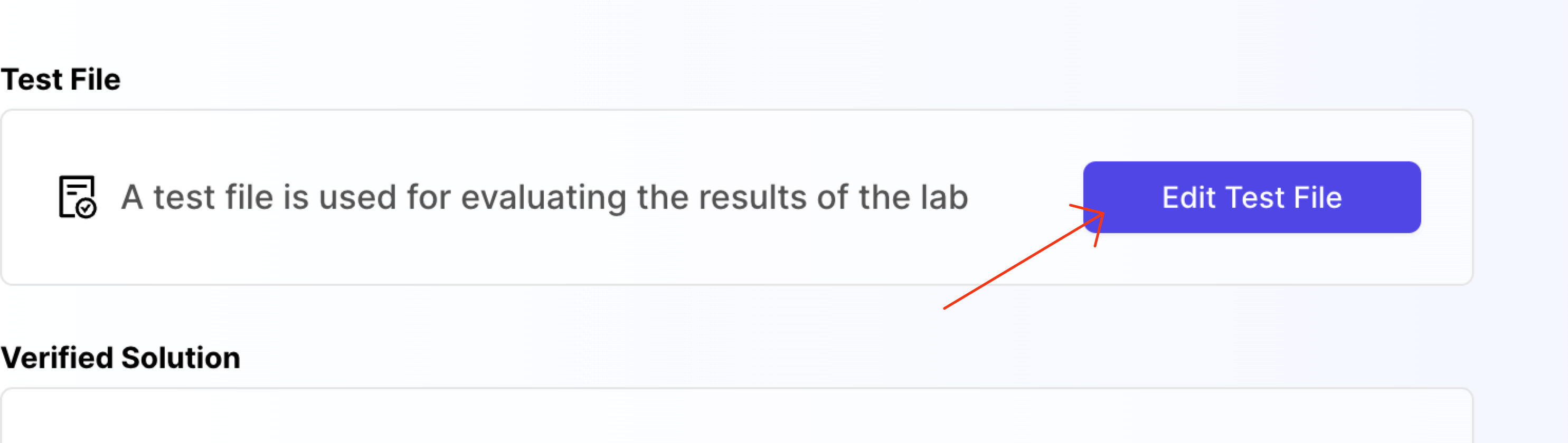
When you click on it, a new window will open. This is a test file area.
You can write anything here. Whatever script you write here, can be executed from the Test command to run section inside the evaluation tab we were in earlier.
The point of having a file like this to provide you with a place where you can write your evaluation script.
Note: For Python labs, I'm assuming you will be using the pre-installed pytest utility to test the user code. Hence, we use the pytest testing format here:
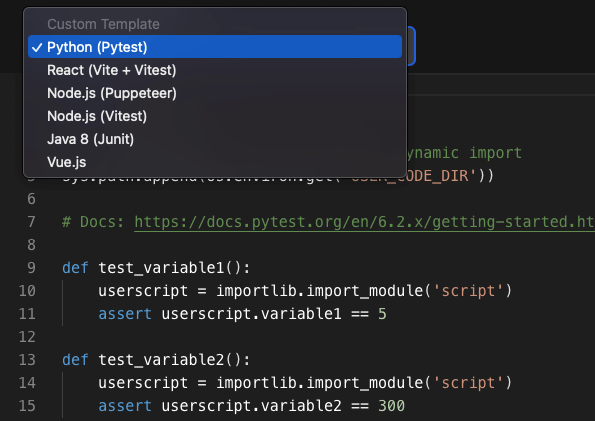
The moment you select the Python (Pytest), the following code should appear in your editor:
import os
import sys
import importlib
# Make user code files available for dynamic import
sys.path.append(os.environ.get('USER_CODE_DIR'))
# Docs: https://docs.pytest.org/en/6.2.x/getting-started.html#create-your-first-test
def test_variable1():
userscript = importlib.import_module('script')
assert userscript.variable1 == 5
def test_variable2():
userscript = importlib.import_module('script')
assert userscript.variable2 == 300Let us understand what is happening here exactly:
- We import some required python packages.
- Then we add
USER_CODE_DIRto thePATHenv.USER_CODE_DIRstring is effectively/home/damner/codewhich in turn is the directory where your students store their coding files (and is also visible in the playground file explorer by default) - We start writing tests on how Python pytest library recommends. Check out pytest documentation for more information.
- We dynamically import the
script.pyusingimportlib.import_module('script'). This is to prevent the test file from crashing other tests in case the script is not there at all. - Then we start asserting based on pytest utilities.
The number of
def test_(...)functions inside your test file suite should match the number of challenges added in the creator area.Note: If your number of
testblocks are less than challenges added back in the UI, the "extra" UI challenges would automatically stay as "false". If you add more challenges in test file, the results would be ignored.
This completes your evaluation script for the lab. Your lab is now almost ready for users.
Step 5 - Evaluation Script
Evaluation script is actually what runs when the user on the codedamn playground clicks on "Run Tests" button.
Remember that we're using the Pytest utility in this lab to test.
Therefore, your testing script would look like as follows:
#!/bin/bash
set -e 1
mkdir -p /home/damner/code/.labtests
mv $TEST_FILE_NAME /home/damner/code/.labtests/user-test-code.py
echo "" > /home/damner/code/.labtests/__init__.py
# Install pytest
pip3 install pytest pytest-json-report
# run test
cd /home/damner/code/.labtests
pytest --json-report user-test-code.py || true
# process results file
cat > processPythonResults.js << EOF
const payload = require('./.report.json')
const answers = payload.tests.map(test => test.outcome === 'passed')
require('fs').writeFileSync(process.env.UNIT_TEST_OUTPUT_FILE, JSON.stringify(answers))
EOF
# Write results to UNIT_TEST_OUTPUT_FILE to communicate to frontend
node /home/damner/code/.labtests/processPythonResults.jsYou might need to have a little understanding of bash scripting. Let us understand how the evaluation bash script is working:
- With
set -e 1we effectively say that the script should stop on any errors - You can install additional packages here if you want. They would only be installed the first time user runs the test. On subsequent runs, it can reuse the installed packages (since they are not removed at the end of testing)
- Then we create a
.labtestsfolder inside of the/home/damner/codeuser code directory. Note that.labtestsis a special folder that can be used to place your test code. This folder will not be visible in the file explorer user sees, and the files placed in this folder are not "backed up to cloud" for user. - We move the test file you wrote earlier (in last step) to
/home/damner/code/.labtests/pytest.py. - We then create another setup file
/home/damner/code/.labtests/processPythonResults.js. This is because we need to parse the results outputted by the Python testing utility to reflect it on the playgrounds. You may as well create this file in python (reading the JSON report and outputting a boolean array in a file stored in env$UNIT_TEST_OUTPUT_FILE) - This is important because on the playground page, the way challenges work, is that they get green or red based on a JSON boolean array written inside the file in environment variable:
$UNIT_TEST_OUTPUT_FILE - For example, once the test run succeeds, and if you write
[true,false,true,true]inside$UNIT_TEST_OUTPUT_FILE, it would reflect as PASS, FAIL, PASS for 3 challenges available inside codedamn playground UI (as shown below)

Then we run the actual test using
python3 -m pytestcommand, specifying the output as JSON (read byprocessPythonResults.js) and in a single thread (as we want ordered results).Finally we run the
processPythonResults.jsfile that writes the correct JSON boolean array on$UNIT_TEST_OUTPUT_FILEwhich is then read by the playground UI and marks the lab challenges as pass or fail.
Note: You can setup a full testing environment in this block of evaluation script (installing more packages, etc. if you want). However, your bash script test file will be timed out after 30 seconds. Therefore, make sure, all of your testing can happen within 30 seconds.
Setup Verified Solution (Recommended)
Verified solution is highly recommended. To setup a verified solution for your lab, once your lab is ready, all you have to do is click on "Test lab", write code that passes your lab, and run that code once.
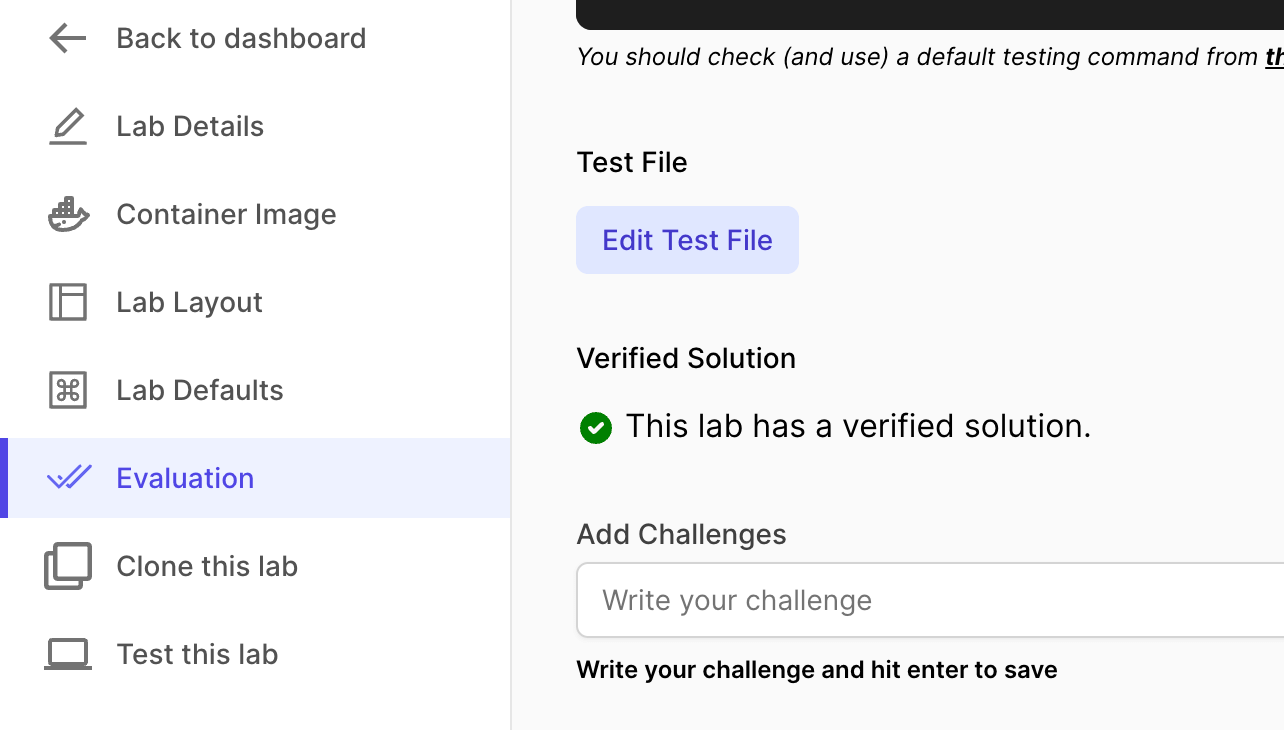
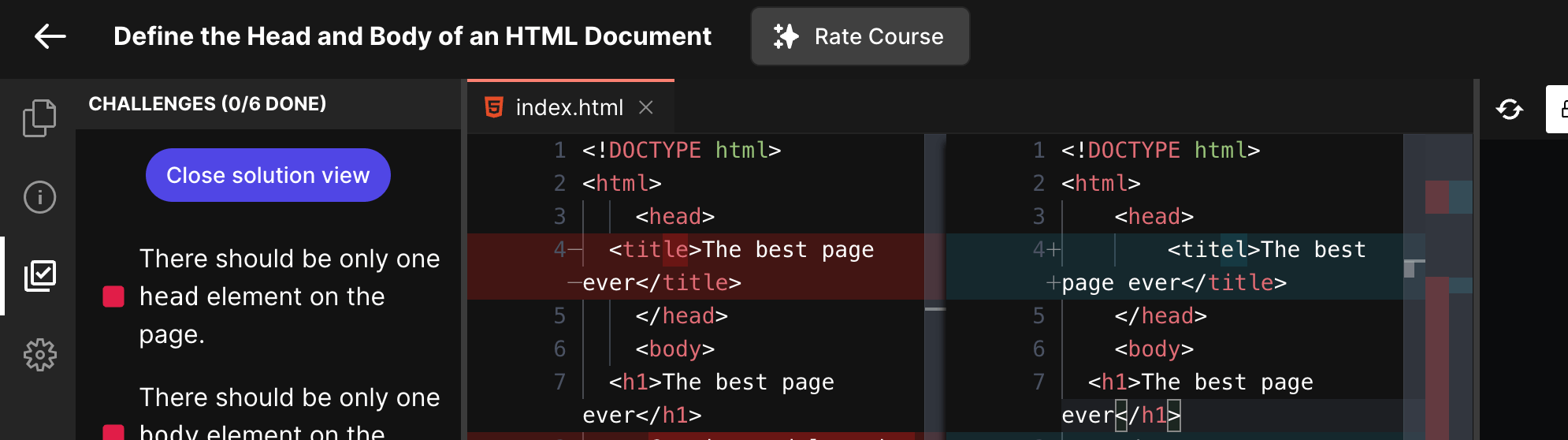
Once you do that, your lab would be marked a lab having verified solution. It also helps students as we can show them a Monaco diff editor showing the verified solution from the creator (you).
At this point, your lab is complete. You can now link this lab in your course, ready to be served to thousands of students 😃 Watch the video tutorial below to understand: